A currency’s interest rate is one of the biggest factor in determining the perceived value of a currency. So understanding how country’s central bank sets its monetary policy, such as interest rates decision, is crucial.
Price stability or inflation is one of the biggest influences on a central banks interest rate decision making.
Inflation – a steady increase in the price of goods and services. – moderate Inflation rates comes with Economic growth. However, too much inflation can harm an economy and that’s why central banks are always keeping a watchful eye on inflation-related economic indicators, Such as CPI; Consumer Price Index (U.S.A) and the PCE; Personal consumption Expenditure – it measures the component statistic for consumption in gross domestic product (GDP) (U.S.A – collected by the bureau of economic analysis.)
- United Kingdom – Bank of England (BOE)
- United States – Federal Reserve System (FED)
- European Union – European Central Bank (ECB)
- Australia – Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)
- Canada – Bank of Canada (BOC)
- Japan – Bank of Japan (BOJ)
- New Zealand – Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ)
- Switzerland – Swiss National Bank (SNB)
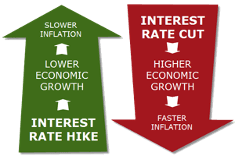
In an effort to keep inflation at a comfortable level, Central Banks will most likely increase Interest Rates, which will most likely result in Lower overall growth and slower Inflation. This occurs because setting high-interest rates normally force consumers and business to borrow less and save more, putting an economic growth in the lower gears. Loans and/or borrowing money becomes more expensive while sitting on cash becomes more attractive and a viable option.
On the other hand, when interest rates are decreasing, consumers and businesses are more inclined to borrow (banks ease lending requirement as an direct result) which most likely increase retail and capital spending, as the price to borrow is lower, which can lead to an economy to grow as more and more people spend.
What does this have to do with the Foreign exchange markets?
Currencies rely on interest Rates because they can dictate the flow of global capital into and out of a country.
Simple Example – if you had a choice of a saving account with either a 0.25% or 1%. You’d choose 1%. Currencies work the same way.
The Higher a country’s interest rate, the more likely its currency will strengthen over the long term. Currencies surrounded by lower interest rates are likely to weaken over the longer term.
Domestic Interest Rates directly affect how global market players feel about a currency’s value relative to another.



